You are currently looking at the v11.0 docs, which are still a work in progress. If you miss anything, you may find it in the older v10.0 docs here.
Build Performance
ReScript considers performance at install time, build time and run time as a serious feature; it's one of those things you don't notice until you realize it's missing.
Profile Your Build
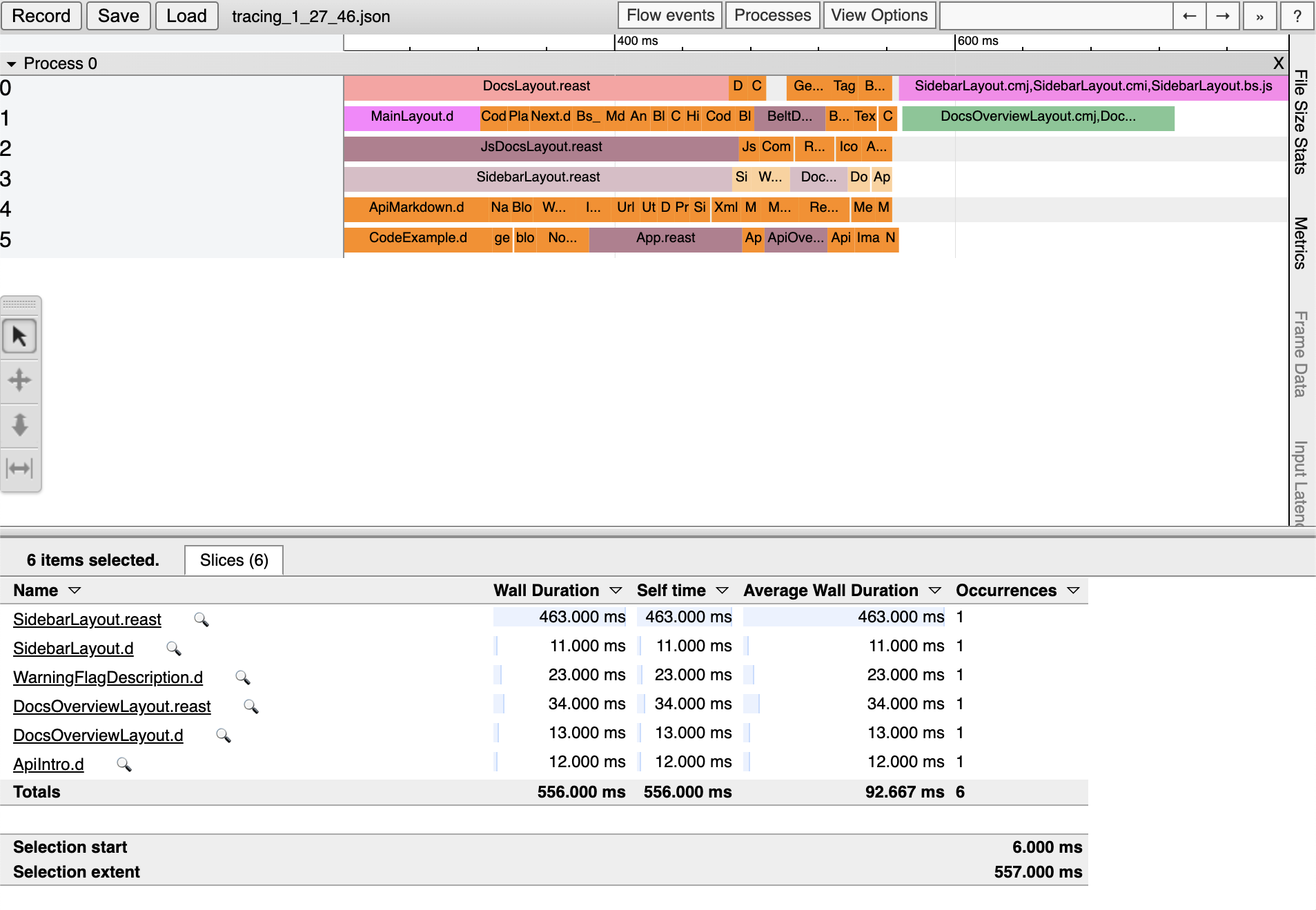
Sometime your build can be slow due to some confused infra setups. We provide an interactive visualization of your build's performance via bstracing:
SH./node_modules/.bin/bstracing
Run the above command at your ReScript project's root; it'll spit out a JSON file you can drag and drop into chrome://tracing.
Under the Hood
ReScript itself uses a build system under the hood, called Ninja. Ninja is like Make, but cross-platform, minimal, focuses in perf and destined to be more of a low-level building block than a full-blown build system. In this regard, Ninja's a great implementation detail for rescript.
ReScript reads into rescript.json and generates the Ninja build file in lib/bs. The file contains the low-level compiler commands, namespacing rules, intermediate artifacts generation & others. It then runs ninja for the actual build.
The JS Wrapper
rescript itself is a Node.js wrapper which takes care of some miscellaneous tasks, plus the watcher. The lower-level, watcher-less, fast native rescript is called rescript.exe. It's located at node_modules/rescript/{your-platform}/rescript.exe.
If you don't need the watcher, you can run said rescript.exe. This side-steps Node.js' long startup time, which can be in the order of 100ms. Our editor plugin finds and uses this native rescript.exe for better performance.
Numbers
Raw rescript.exe build on a small project should be around 70ms. This doubles when you use the JS rescript wrapper which comes with a watcher, which is practically faster since you don't manually run the build at every change (though you should opt for the raw rescript.exe for programmatic usage, e.g. inserting rescript into your existing JS build pipeline).
No-op build (when no file's changed) should be around 15ms. Incremental rebuild (described soon) of a single file in a project is around 70ms too.
Cleaning the artifacts should be instantaneous.
Extreme Test
We've stress-tested rescript.exe on a big project of 10,000 files (2 directories, 5000 files each, first 5000 no dependencies, last 5000 10 dependencies on files from the former directory) using https://github.com/rescript-lang/build-benchmark, on a Retina Macbook Pro Early 2015 (3.1 GHz Intel Core i7).
No-op build of 10k files:
800ms(the minimum amount of time required to check the mtimes of 10k files).Clean build: <3 minutes.
Incremental build: depends on the number of the dependents of the file. No dependent means
1s.
Stability
rescript is a file-based build system. We don't do in-memory build, even if that speeds up the build a lot. In-memory builds risk memory leaks, out-of-memory errors, corrupt halfway build and others. Our watcher mode stays open for days or months with no leak.
The watcher is also just a thin file watcher that calls rescript.exe. We don't like babysitting daemon processes.
Incrementality & Correctness
ReScript doesn't take whole seconds to run every time. The bulk of the build performance comes from incremental build, aka re-building a previously built project when a few files changed.
In short, thanks to our compiler and the build system's architecture, we're able to only build what's needed. E.g. if MyFile.res isn't changed, then it's not recompiled. You can roughly emulate such incrementalism in languages like JavaScript, but the degree of correctness is unfortunately low. For example, if you rename or move a JS file, then the watcher might get confused and not pick up the "new" file or fail to clean things up correctly, resulting in you needing to clean your build and restart anew, which defeats the purpose.
Say goodbye to stale build from your JavaScript ecosystem!
Speed Up Incremental Build
ReScript uses the concept of interface files (.resi) (or, equivalently, module signatures). Exposing only what you need naturally speeds up incremental builds. E.g. if you change a .res file whose corresponding .resi file doesn't expose the changed part, then you've reduced the amount of dependent files you have to rebuild.
Programmatic Usage
Unfortunately, JS build systems are usually the bottleneck for building a JS project nowadays. Having parts of the build blazingly fast doesn't matter much if the rest of the build takes seconds or literally minutes. Here are a few suggestions:
Convert more files into ReScript =). Fewer files going through fewer parts of the JS pipeline helps a ton.
Careful with bringing in more dependencies: libraries, syntax transforms (e.g. the unofficially supported PPX), build step loaders, etc. The bulk of these dragging down the editing & building experience might out-weight the API benefits they provide.
Hot Reloading
Hot reloading refers to maintaining a dev server and listening to file changes in a way that allows the server to pipe some delta changes right into the currently running browser page. This provides a relatively fast iteration workflow while working in specific frameworks.
However, hot reloading is fragile by nature, and counts on the occasional inconsistencies (bad state, bad eval, etc.) and the heavy devserver setup/config being less of a hassle than the benefits it provides. We err on the side of caution and stability in general, and decided not to provide a built-in hot reloading yet. Note: you can still use the hot reloading facility provided by your JS build pipeline.